Enterprise-grade vs Hardened-grade Ethernet Switches — which is best for your project?
Ethernet switches primarily fit into two categories: enterprise grade and hardened grade.
Enterprise-grade switches are typically rack-mounted or desktop switches, depending on the number of ports. These switches are normally at the edge in the access layer of an enterprise network or used as a standard switch in the small office environment. An enterprise-grade switch is designed to function in a controlled environment where the switch temperature is constant, and the switch is protected from harsh environmental conditions.
Hardened-grade switches are designed for harsh environments in which the switch is likely to be placed in an uncontrolled environment with varied temperatures, dust and other environmental conditions. A Hardened-grade Ethernet switch is specifically designed to work in these harsh environments.
Both enterprise-grade and hardened-grade Ethernet switches contain features such as VLANs, Quality of Service (QoS), Power over Ethernet (PoE) and management via Web GUI, CLI or SNMP. In fact, if you were to log into an enterprise-grade switch and a hardened-grade switch, you would find the same commands, look and feel between the products and likely would not notice any major configuration differences.
What are the differences between enterprise-grade and hardened-grade switches?
1. Form Factor
Hardened-grade switches are typically DIN rail mounted as opposed to rack-mount enterprise-grade switches. The DIN rail installation of hardened-grade switches helps make them more resistant to shock and vibration, which is often required for hardened-switch applications.
2. Operating temperature
Enterprise-grade switches are designed for controlled environments, such as offices. An enterprise-grade switch has a normal operating temperature of 0–50 degrees Celsius. While this temperature works fine in a controlled office environment, it does not work for harsh environments. Hardened-grade switches are designed to work in temperatures from -40–75 degrees Celsius. This makes hardened-grade switches more versatile for uses in factories, outdoor environments and industrial automation.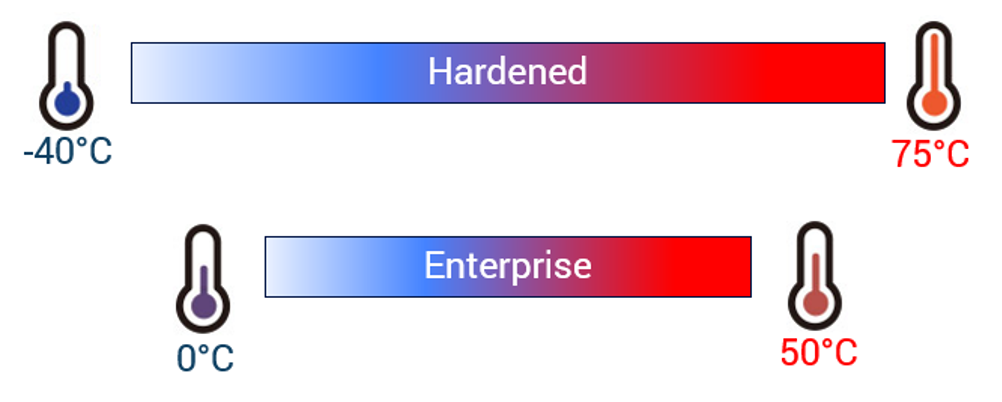
3. Power
Enterprise-grade switches normally rely on a single power supply within a stable environment in which networks are protected from power failures and only work with AC voltage. Larger port count and higher-end enterprise-grade switches will have the option of redundant AC power supplies.
Hardened-grade switches will have redundant power inputs and operate on DC voltage.
4. Reliability
Hardened-grade switches are not affected by items like ambient temperatures, humidity, dust, vibration or shock. Because of this, hardened-grade switches will have a higher Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF), which means the elapsed time between inherent failures of electronic systems. This is all achieved without maintenance or requiring replacement parts. An enterprise-grade switch MTBF is dependent on the operating temperature and environment in which it is used.
5. Fanless
Hardened-grade switches use a fanless enclosure to dissipate all the heat from the actual hardware while enterprise-grade switches use fans for cooling. Hardened-grade switches are also quieter due to no fan noise. Fanless hardened-grade switches are also beneficial in uncontrolled environments that may be dusty and dirty since fans would require more maintenance due to dust accumulation.
Summary
Enterprise-grade and hardened-grade switches have the same feature and functionality but accommodate different environments. If the switch is going to be in an uncontrolled, dusty or dirty environment, a hardened-grade Ethernet switch will ensure that the network keeps functioning.




